We live in a crazy world that seems to grow crazier by the day. But we must not let the chaos get to us. We need to carry on as best we can. For me, photography is one outlet that shuts out the din of the world’s madness against itself.
I enjoy photographing the wonder all around me, the serendipitous joy that springs upon me. By capturing those affectionate moments, I can share them with others, including you.
Staying in the present moment allows me to see things that others might just pass by. Consequently, I took thousands of photos this year. My photos feature people, insects, birds, trees, mountains, flowers, sunsets, sunrises, boats, planes, and a sundry of other subjects.
I have chosen to select one image for each month to review 2025. I hope each photo speaks to you the way they all did to me. Here then is 2025 in photos. Enjoy.
January
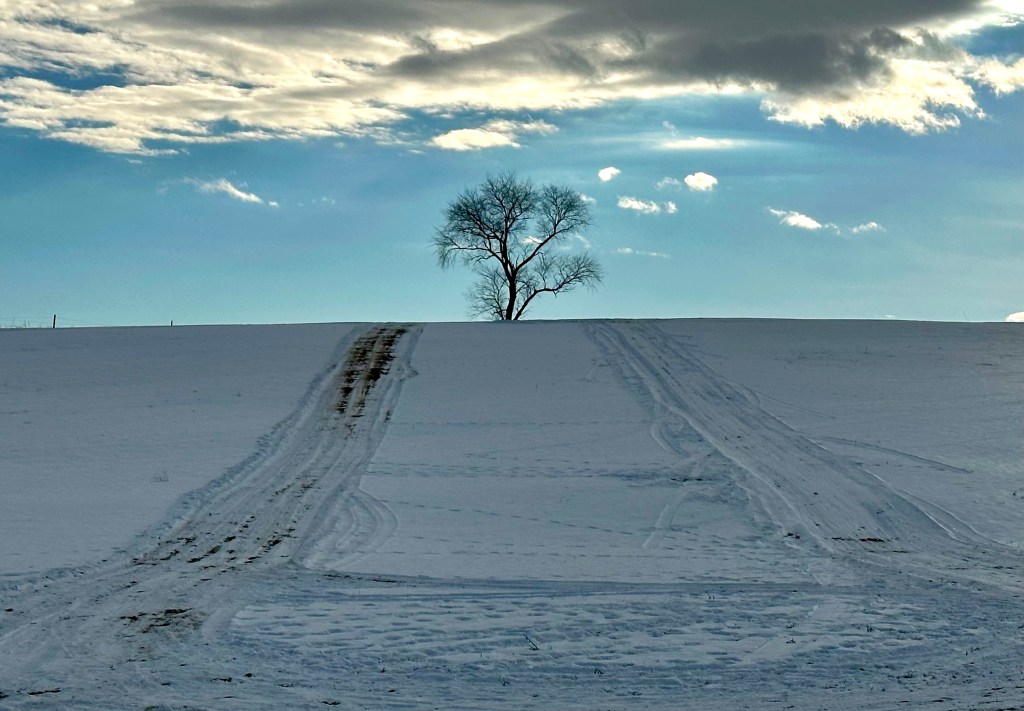
It’s only appropriate to begin this photo series with a snowy scene in January. This lone tree stood beneath the hovering clouds and was perfectly centered by the farm equipment tracks in the snow. The cerulean sky provided an excellent backdrop, like blue ice in a glacier.

February
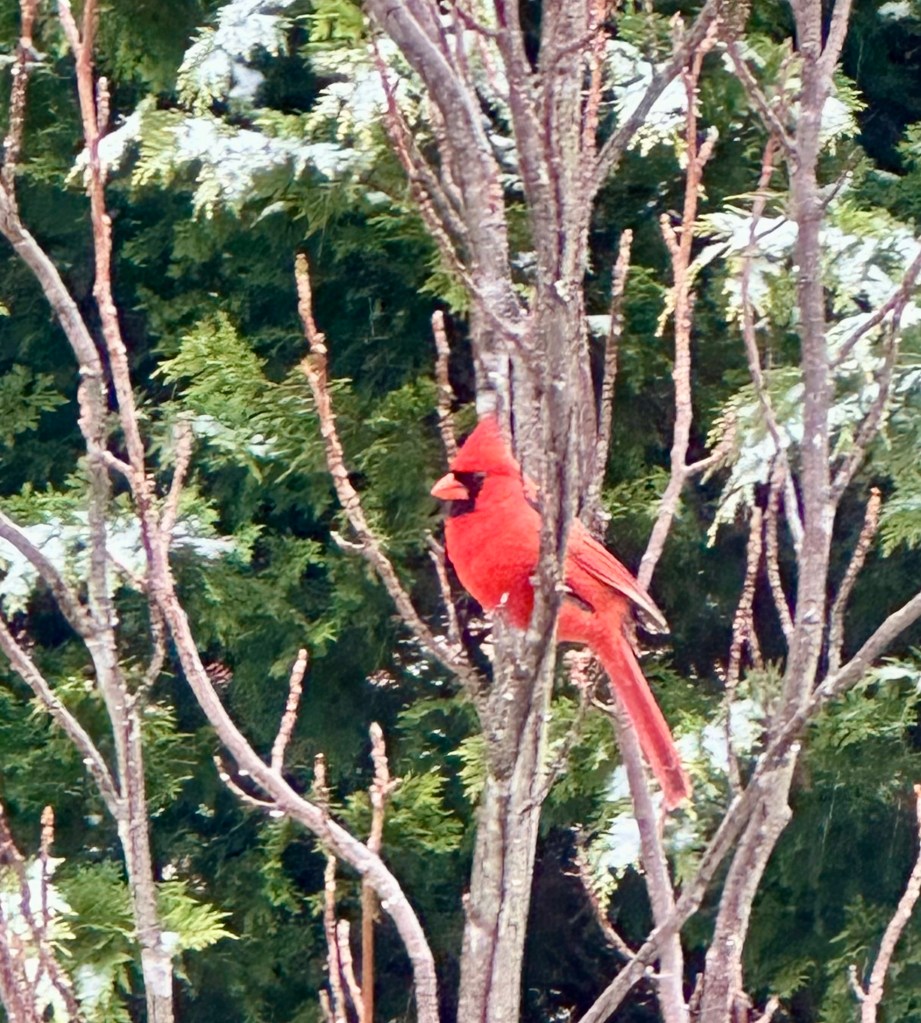
Is there anything more stunning than a bright red male Northern Cardinal in the midst of winter? Against evergreens laden with a skiff of snow, the bird shows even more colorfully. It’s just one of the reasons I love watching, feeding, and photographing birds.
That’s especially true when they grace your backyard with such natural beauty.

March
I enjoy walking in our suburban neighborhood of nearly 500 homes any time of year. Besides the required exercise, I encounter many photographic moments. This neighbor had the foresight to plant daffodil bulbs around an old hand cultivator, once used to till garden soil, which helped control the weeds.
Emerging from winter, the buttery yellow of the blooms added a splash of color that complemented the old, rusting implement.
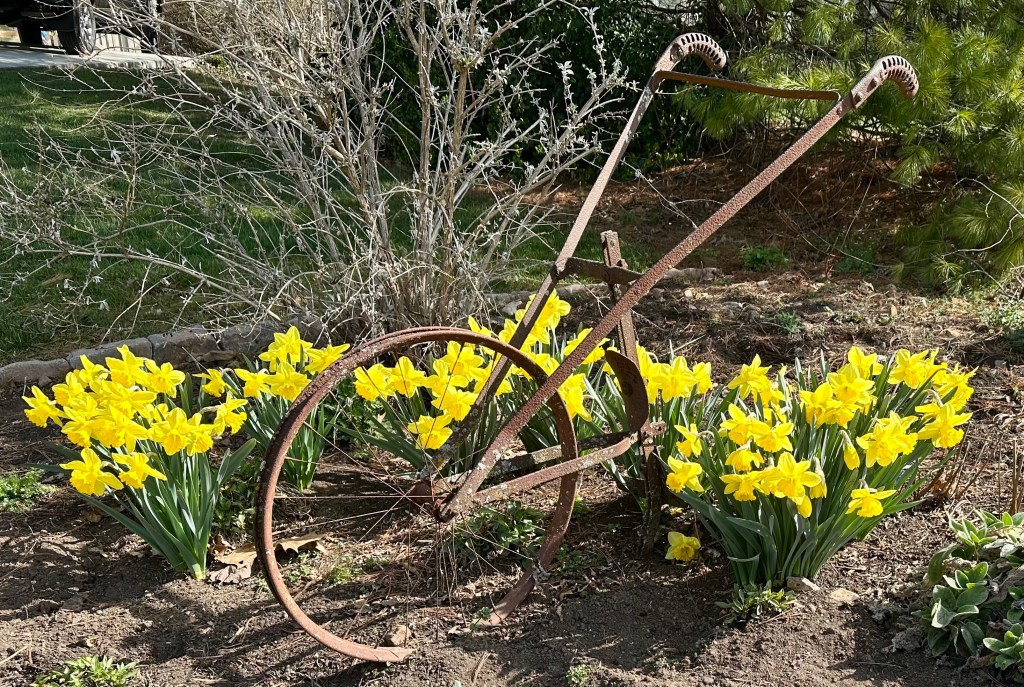
April
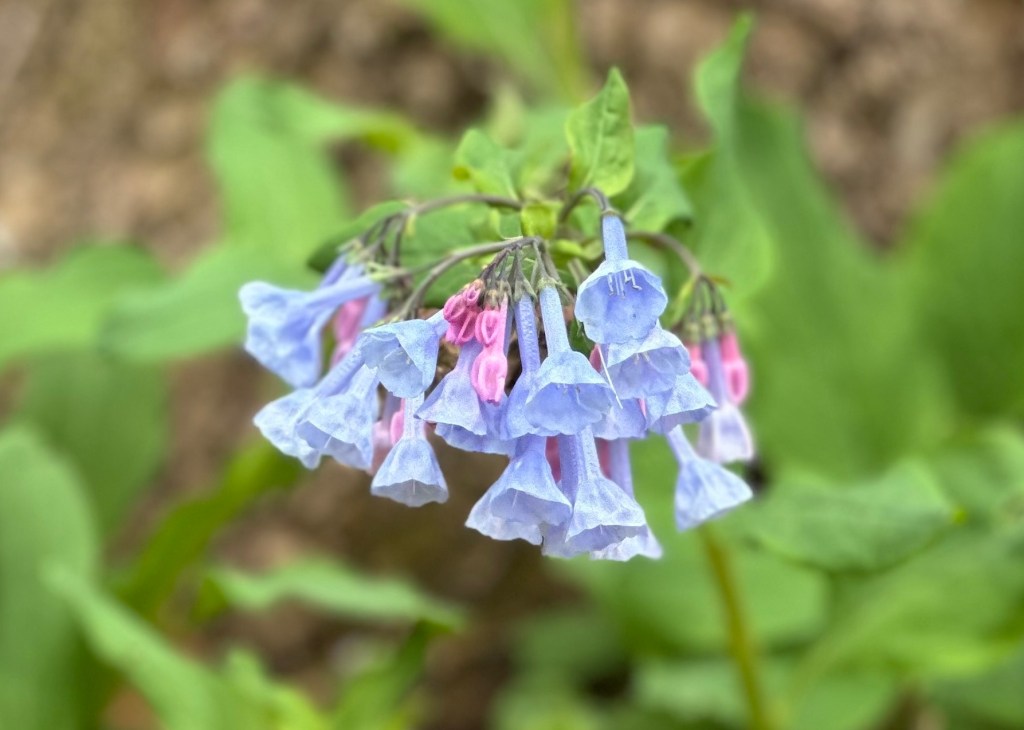
Though not the state flower, Virginia Bluebells should be. They are native to the state and are its namesake. Besides that, the flowers are simply beautiful. Their pink buds turn to azure blue blossoms, and they are a welcome sight wherever they bloom in spring.

May
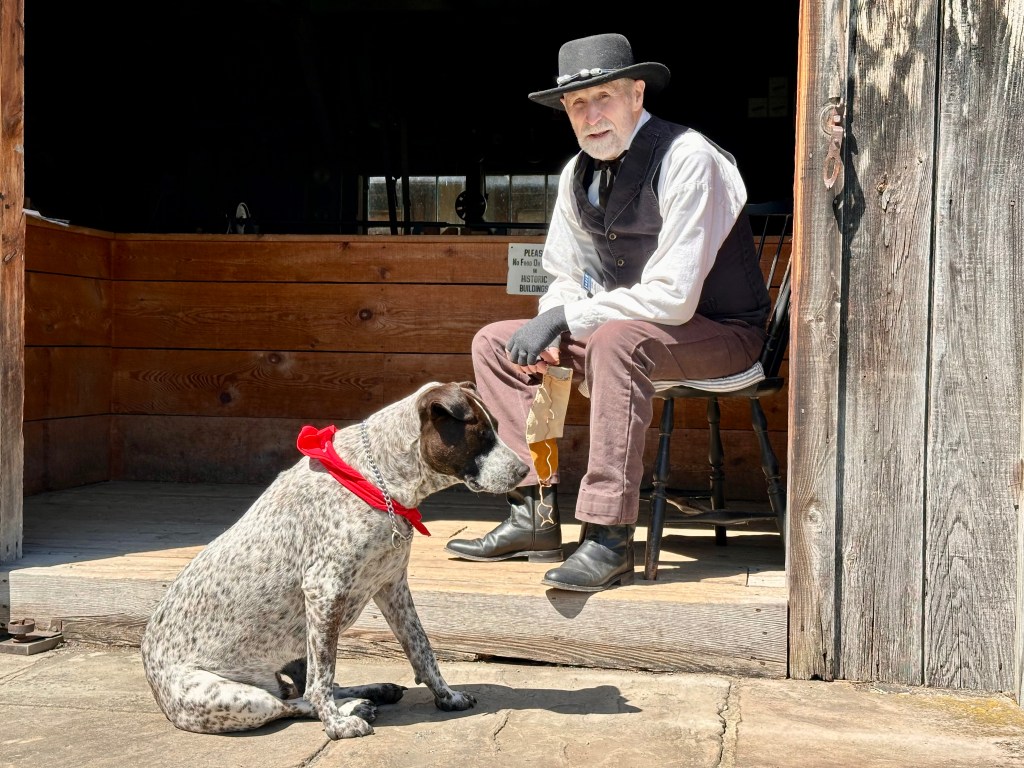
I captured this photo at a historic village in Mumford, New York. Since it was Mother’s Day, the Genese Country Village and Museum had people in period clothing doing demonstrations and providing information about their particular station.
While walking by a barn, I caught this man and his dog sitting in the morning sunshine. The darkness of the barn’s interior made them stand out all the more.

June
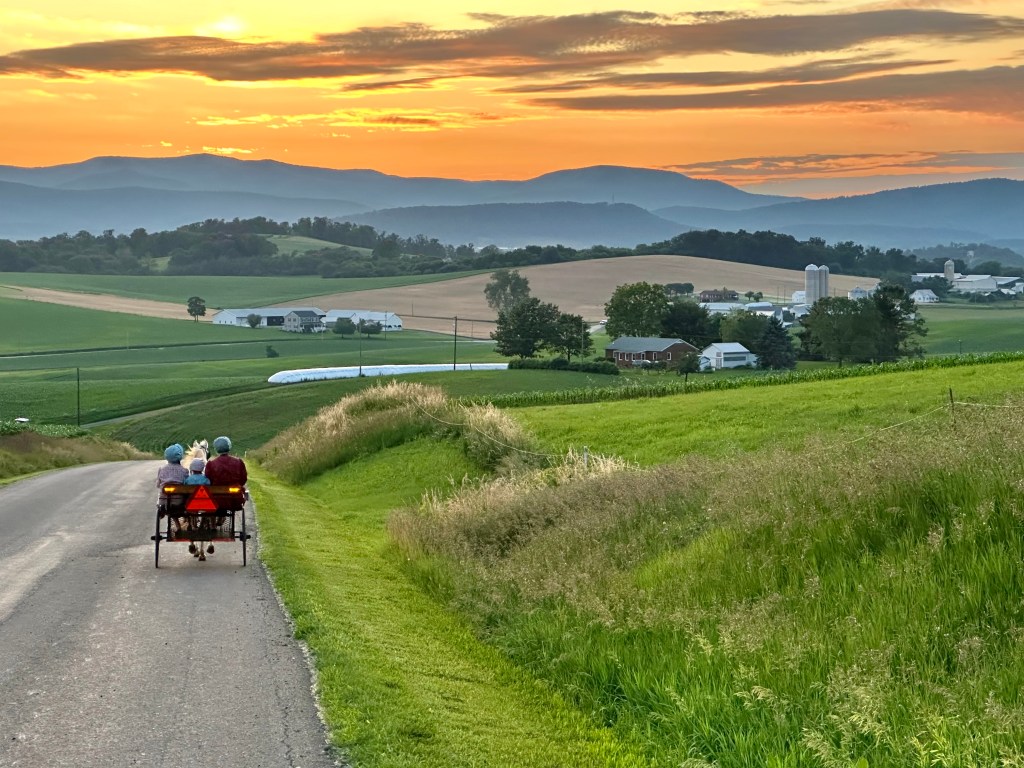
I’m a sucker for sunsets. With its fluffy-cloud days, June is often a good time to watch for glowing evening skies. June 20th was one such day. It just happened to be the summer solstice, when the sun would be at its northwestern-most point in the evening sky.
I headed to my favorite photo spot, the western slope of a local landmark, Mole Hill. Mole Hill is a prominent mound in Shenandoah Valley’s Rockingham County. You can see miles south, west, and northwest from the extinct volcanic core.
On the way there, I saw a pony cart tied to the trunk of a walnut tree at the peak of Mole Hill Road. I didn’t think much of it until I heard the distinct sound of hoves hitting the pavement. I turned and saw an Old Order Mennonite young woman and two girls in an open cart behind a blond-maned pony heading my way.
Knowing they would not want their photo taken, I waited until the cart was well past my location before I snapped the shutter. The setting sun illuminated the pony’s mane and the seeded heads of the tall grass north of the roadway.
With the evening quickly cooling, a light fog began lifting out of the river valley below the Allegheny Mountains that mark the boundary between Virginia and West Virginia.
The combination of the golden sky, the glowing clouds, the darkened mountains, the mist, the farmsteads, and the rolling valley floor created a once-in-a-lifetime scene. It felt like a holy moment, and I was thrilled to capture it for others to see.

July
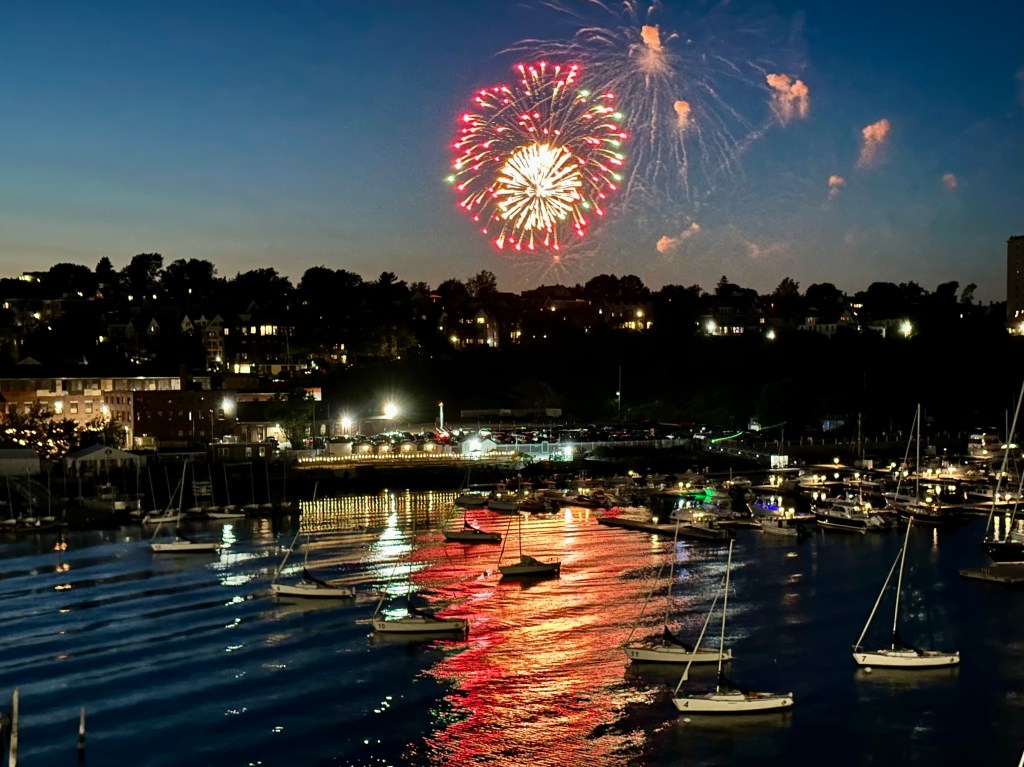
In the United States, July literally always starts out with a bang. July 4th is Independence Day, and it just so happened that the cruise ship my wife and I were on docked in Portland, Maine, on that hallowed day.
Fortunately, the ship’s starboard side, where our cabin was, faced the city’s harbor. We had a front-row seat to all the explosive colors reflected in the water. It was a fun way to close out our trip.

August
Like many other locales in the nation, August was a hot, humid, and all too dry month. Still, people ventured out, keeping their routines and schedules despite the withering temperatures.
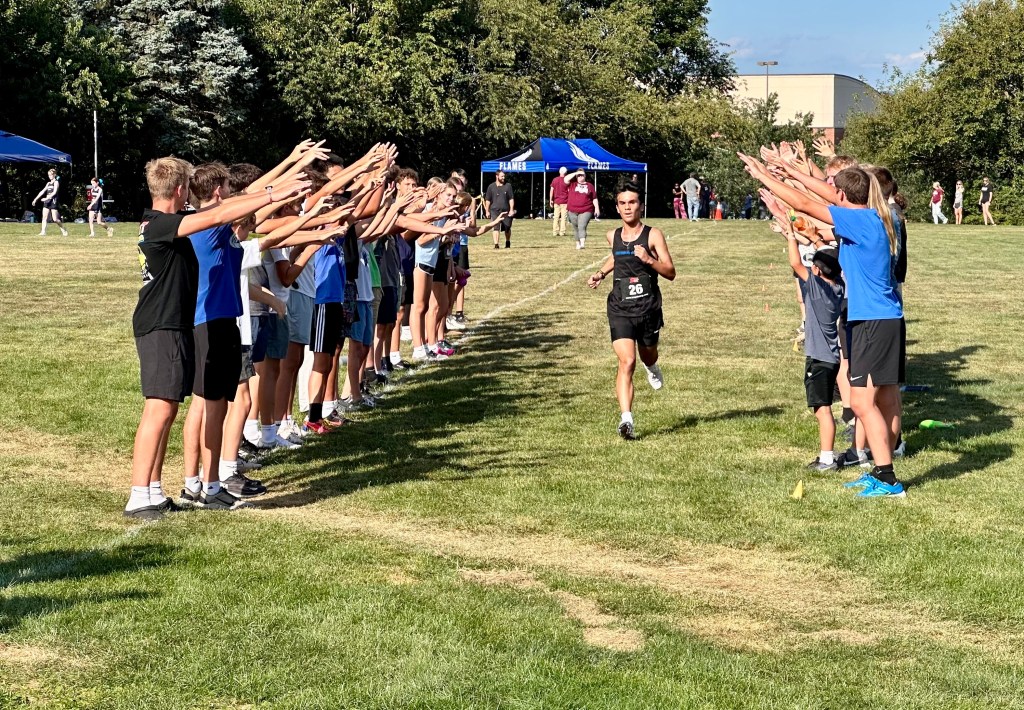
That was true for all kinds of outdoor sports. This photo shows the proud moment of the young man I mentor, far outpacing all the other high school runners in a cross-country meet. I wasn’t the only one who was pleased. Daniel’s classmates created a human gauntlet to welcome him as he approached the finish line.

September
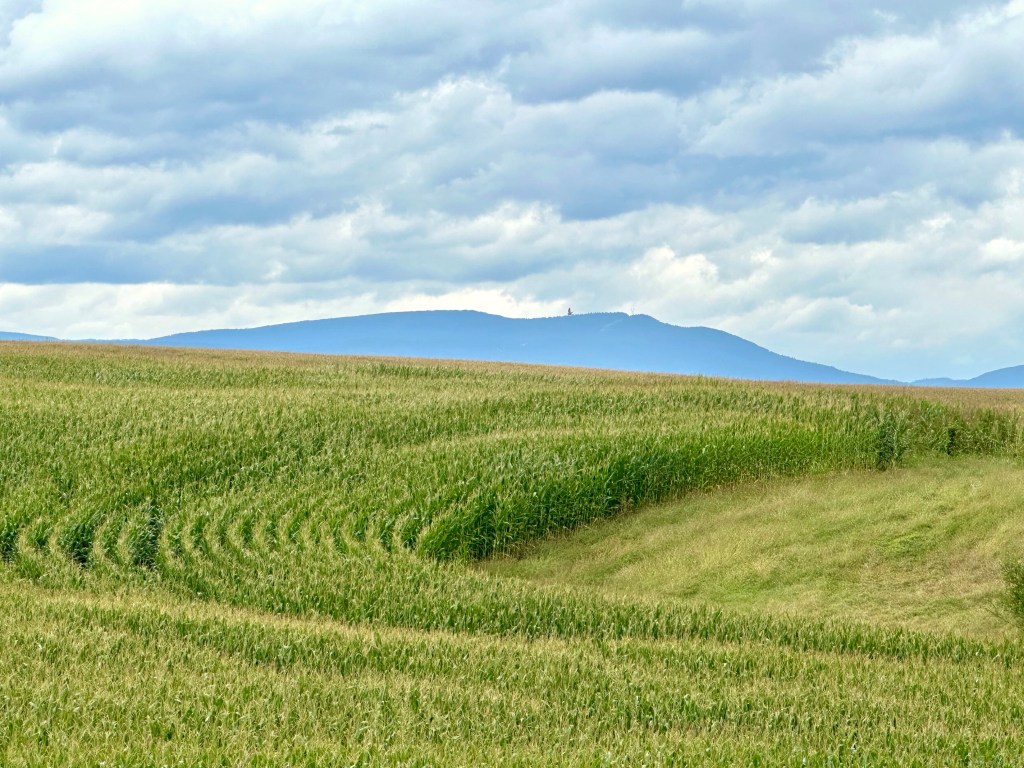
This September in Virginia’s lovely Shenandoah Valley was fabulous. After a hot, humid summer, September ushered in cooler temperatures and revealed the magnificent colors of her topography and vegetation, both natural and cultivated.
This was the view I saw as I exited my vehicle at a country store near the quaint town of Dayton. How could I not take this shot?
From the area’s fertile soil, curving rows of field corn and rolling contours led the eye to the Allegheny Mountains to the northwest and the cruising cumulus clouds above. Come harvest, it was a bumper crop of corn.
Though I didn’t see it at the time, an American Crow is near dead center in the pastoral photo.

October
Our three-year-old grandson loves Halloween. He also loves bubbles, so his folks bought him a bubble machine. Teddy wanted to show off how the bubble maker worked when we visited him and his parents the week of Halloween.
When Teddy ran behind the bubbles, the sharply slanting sun highlighted the multi-colored, windblown bubbles. The various-sized bubbles and their proximity to my camera created a moment I can’t forget. It was one of my favorites of the year.
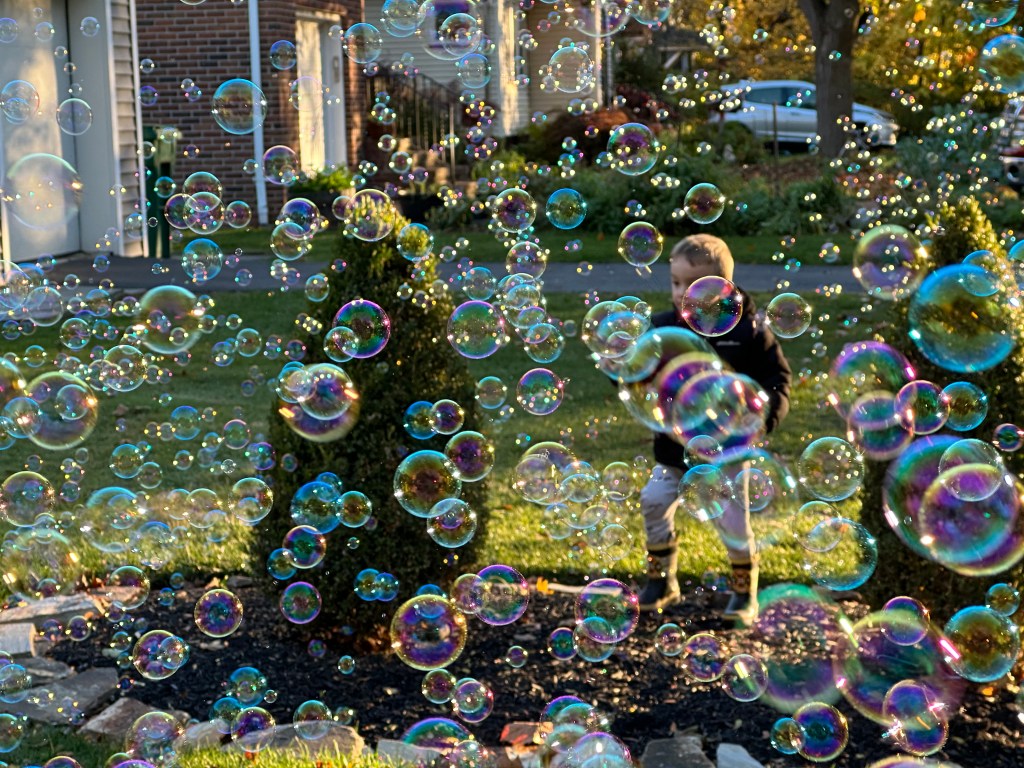
November
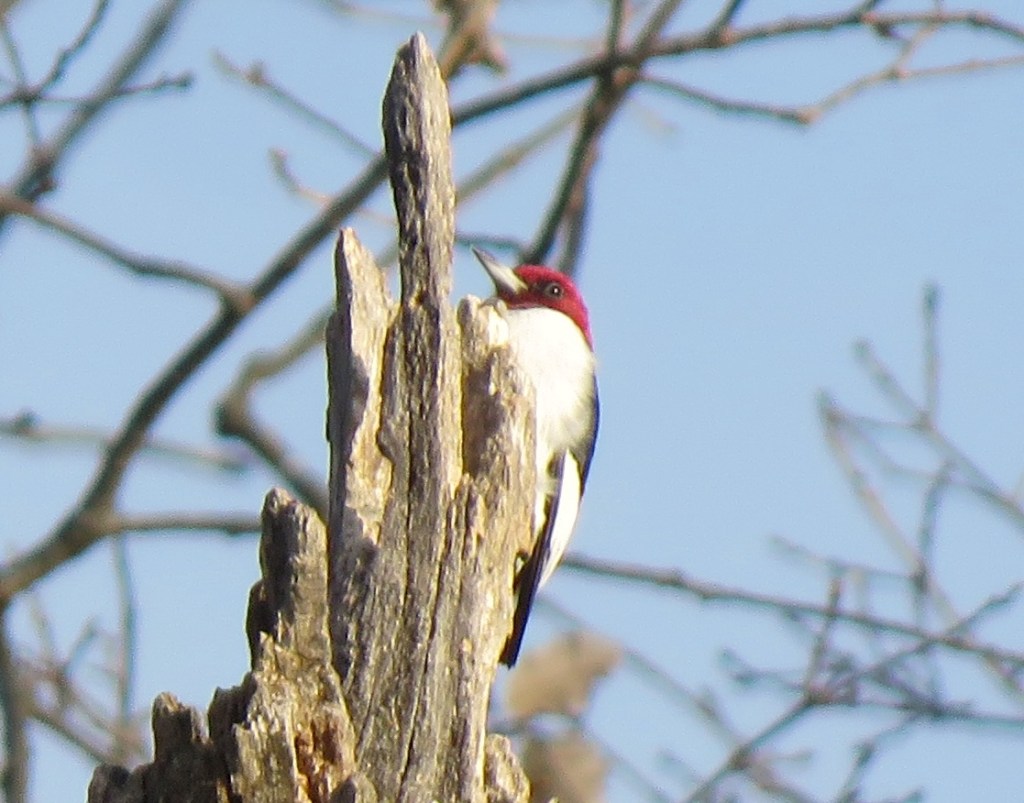
When a Red-headed Woodpecker poses for you, you have to take the shot. Of course, I am always ready with the camera when the moment arrives.

December
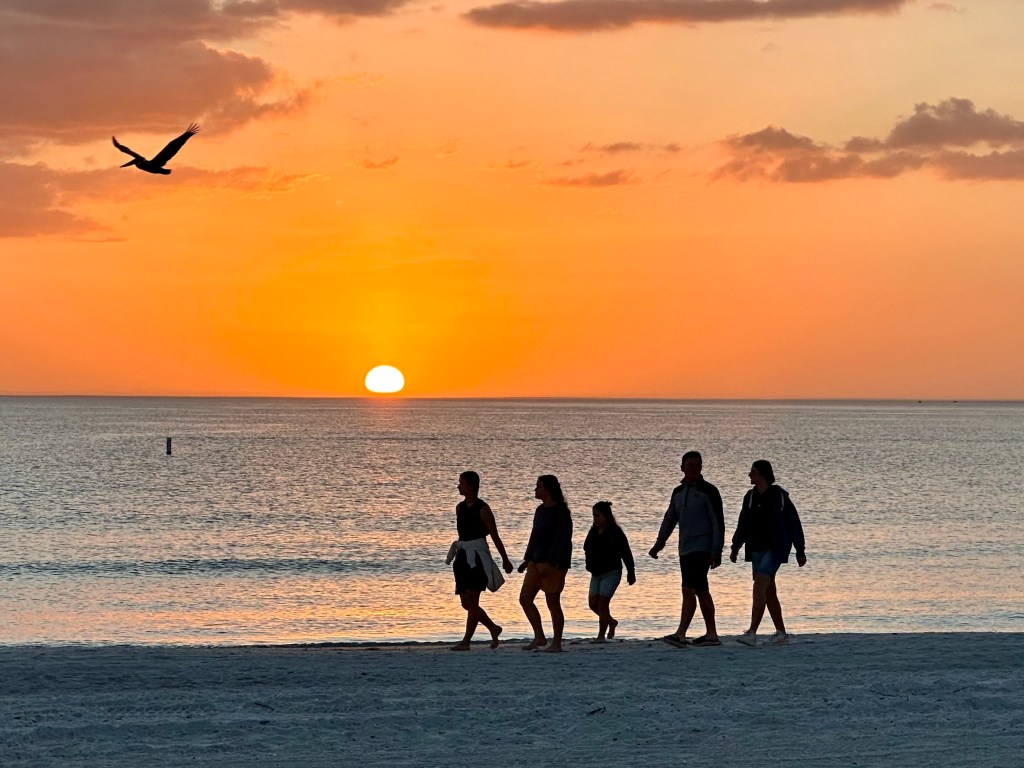
My wife and I spent Christmas week in Sarasota, Florida, with our daughter and her family. We wanted to devote holiday family time together somewhere warm. I’m happy to say the weather was perfect. With two college-aged grandsons and a teenage granddaughter, we hit the beach a few times.
After basking in the warm sunshine during the day, we returned a couple of times for the sunset. When the clouds didn’t cooperate, we settled for golden sundowns.
In this photo, a Brown Pelican appears to be leading the way home for this family walking along North Lido Beach. Sometimes the photo paints the picture for you. Plus, it’s only appropriate that we let the sun set on 2025.

I hope you and yours have a joyous and safe New Year.
© Bruce Stambaugh 2025



















































You must be logged in to post a comment.